Pipeline
Introduction#
- A Guzzle Pipeline represents a cohesive collection of activities that collaborate to accomplish a specific task.
- By utilizing a Pipeline, you gain the ability to manage activities as a unified entity, rather than dealing with each activity independently. This allows for easier deployment and scheduling of the Pipeline as a whole, rather than managing individual activities separately.
- Activities within a Pipeline define the specific actions performed on the data. For instance, you can employ a Guzzle Ingestion activity to transfer data from an Azure Blob Storage to a Delta table. Subsequently, a Processing activity can be used to process and transform the data within the Delta table, which serves as the foundation for building business intelligence reporting solutions.
- Guzzle Pipelines support multiple groupings of activities, including Ingestion, Processing, Constraint Check, Reconciliation, and External activities. These groupings enable you to organize and structure your data processing workflow effectively.
Guzzle Pipeline Types#
- Guzzle Pipeline:
- The Guzzle Pipeline is a standard pipeline that is executed and orchestrated directly through the Guzzle API. It provides a straightforward approach for defining and managing pipelines within the Guzzle framework. The Guzzle API takes care of the pipeline's execution and coordination.
- Databricks Multitask Pipeline:
- The Databricks Multitask Pipeline is a pipeline type supported by Guzzle. In this pipeline, Guzzle prepares and submits a collection of activities with their dependencies to Databricks. Databricks takes over the orchestration and execution of the pipeline, leveraging its powerful capabilities for distributed processing and resource management.
- Manual DAG Pipeline:
- In Guzzle, a Manual DAG (Directed Acyclic Graph) workflow represents a data processing pipeline where you explicitly define the dependencies and execution order of individual activity. This pipeline type requires you to construct a directed graph structure, specifying the relationships and dependencies between activity. By defining the DAG manually, you have fine-grained control over the execution flow of the pipeline.
Each of these pipeline types offers unique features and capabilities to suit different requirements and use cases within the Guzzle framework. Choose the appropriate pipeline type based on the specific needs of your data processing workflows.
Within each of these pipelines, users have the ability to configure a static list of activities along with their parameters and override compute configurations. This allows for fine-tuning and customization of the pipeline execution.
Furthermore, Guzzle Pipeline and Databricks Multitask Pipeline support Dynamic Pipeline configuration, which offer enhanced flexibility and adaptability. Dynamic Pipelines enable the creation of pipelines with activities that can be dynamically generated at runtime, allowing for more dynamic and responsive data processing workflows. For detailed information on Dynamic Pipelines, refer to the provided link here.
Creating and Configuring Pipelines in Guzzle#
This section provides a step-by-step guide on how to create and configure pipelines in Guzzle. Please follow the instructions below:
- Creating a Pipeline:
- To create a new pipeline, navigate to the Pipelines section on the left sidebar of the Author screen.
- Click on the action menu (...) button or the "New" button below "Quick Search." This action will open the "Create New Pipeline" dialog box.
- Specify a name for the pipeline in the provided box.
- Pipeline Configuration:
- It will open Pipeline Configurations tab with pipeline name where you can define the necessary settings and parameters based on your requirements.
- Adding Activities to the Pipeline:
- Add activities to the pipeline by selecting them from the drop-down menu under the "Activities" column.
- Alternatively, you can drag and drop activities from the left sidebar directly into the pipeline.
- Specify activity parameters by clicking on the respective cell under the "Activity Parameter" column.
- Adding Dynamic Activities:
- Dynamic activities can be included in the pipeline to enhance flexibility and adaptability. Details on adding dynamic activities are covered here.
- Modifying Spark Settings:
- Adjust Spark settings for individual activities by clicking on the "Settings" button.
- To modify Spark and execution-related settings globally for the entire pipeline, click the "Settings" button located in the top right corner of the Pipeline editor.
- Refer to the section on specifying these settings for detailed information.
- Generating Pipeline Dependency Graph:
- Guzzle provides the capability to generate a Pipeline Dependency Graph, also known as a Lineage or Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) of the pipeline.
- To generate the graph, go to the dependency section and choose the appropriate option.
- Guzzle will generate a visual representation showing the relationships between different activities within the pipeline.
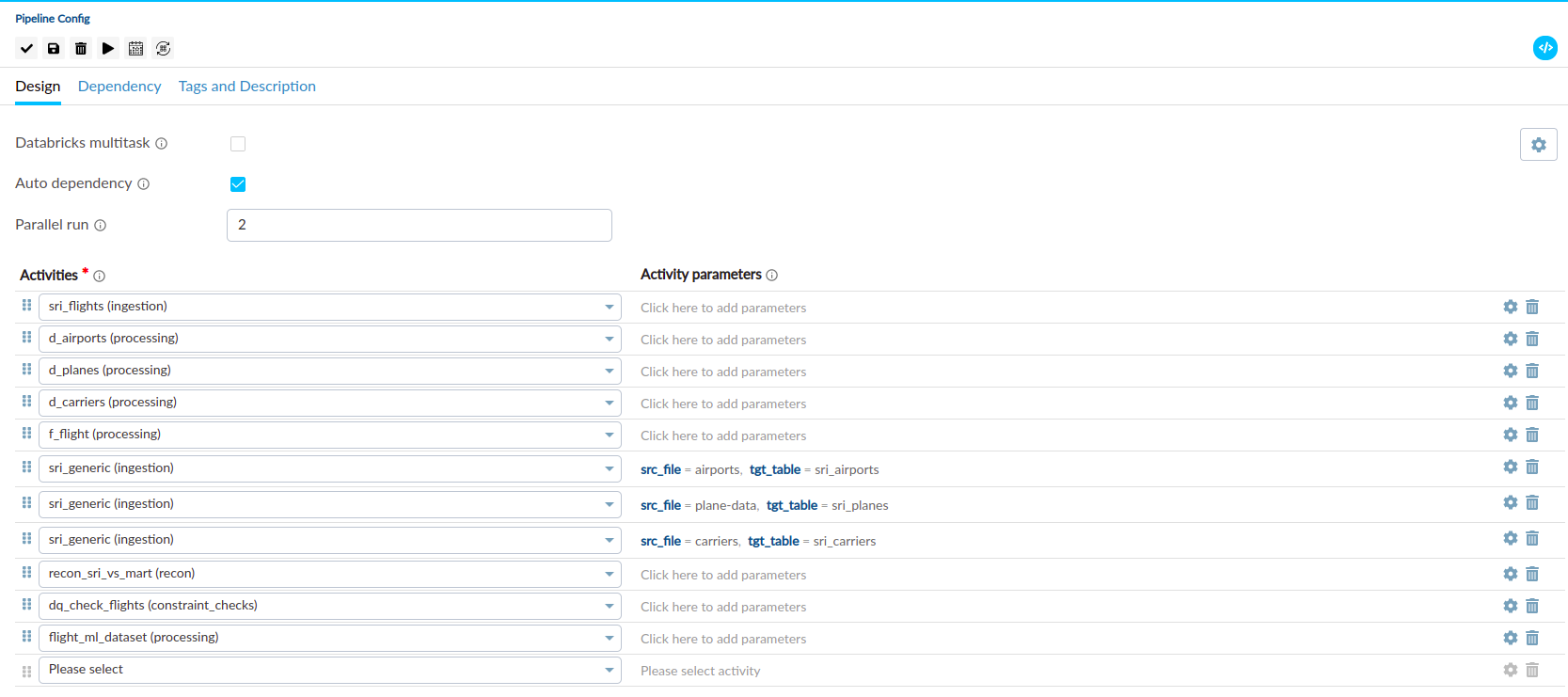
Pipeline Configurations#
| Properties | Description |
|---|---|
| Databricks Multitask Pipeline | The Databricks Multitask Pipeline feature is supported by Guzzle. This feature enables the submission of an entire pipeline as a single workflow in Databricks. Additionally, it provides support for advanced Databricks features such as reusing job clusters across multiple jobs. |
| Auto Dependency | Auto Dependency determines the dependency between subsequent activities based on the previous activities. It defines the condition for continuing the execution of the next task. To perform a second activity on the data generated from the output of the first activity, it is necessary to select the Auto Dependency option. |
| Parallel Run | The Parallel Run feature specifies the number of Guzzle activities to run in parallel within a pipeline. For example, if the parallel run configuration is set to 3, Guzzle will execute three activities simultaneously in the pipeline. |
| Override Spark Settings | Users have the ability to customize compute and Spark configurations at the pipeline level. By default, these configurations will be applied to all activities configured within the pipeline. However, users also have the flexibility to override these settings at the activity level, allowing for specific configurations tailored to individual activities. To gain a deeper understanding of Spark settings and their customization, please refer to the Spark Parameter Documents |
| Computes | By utilizing the "Add New Compute" feature, users can incorporate new Databricks computes into their pipeline. These computes can be assigned to specific activities within the pipeline by accessing the activity settings. It's worth noting that multiple activities can leverage a shared compute cluster for execution, enabling efficient resource utilization and workload management within the pipeline. This feature is specific to Databricks multitask pipelines and cannot be utilized in other pipeline configurations. |
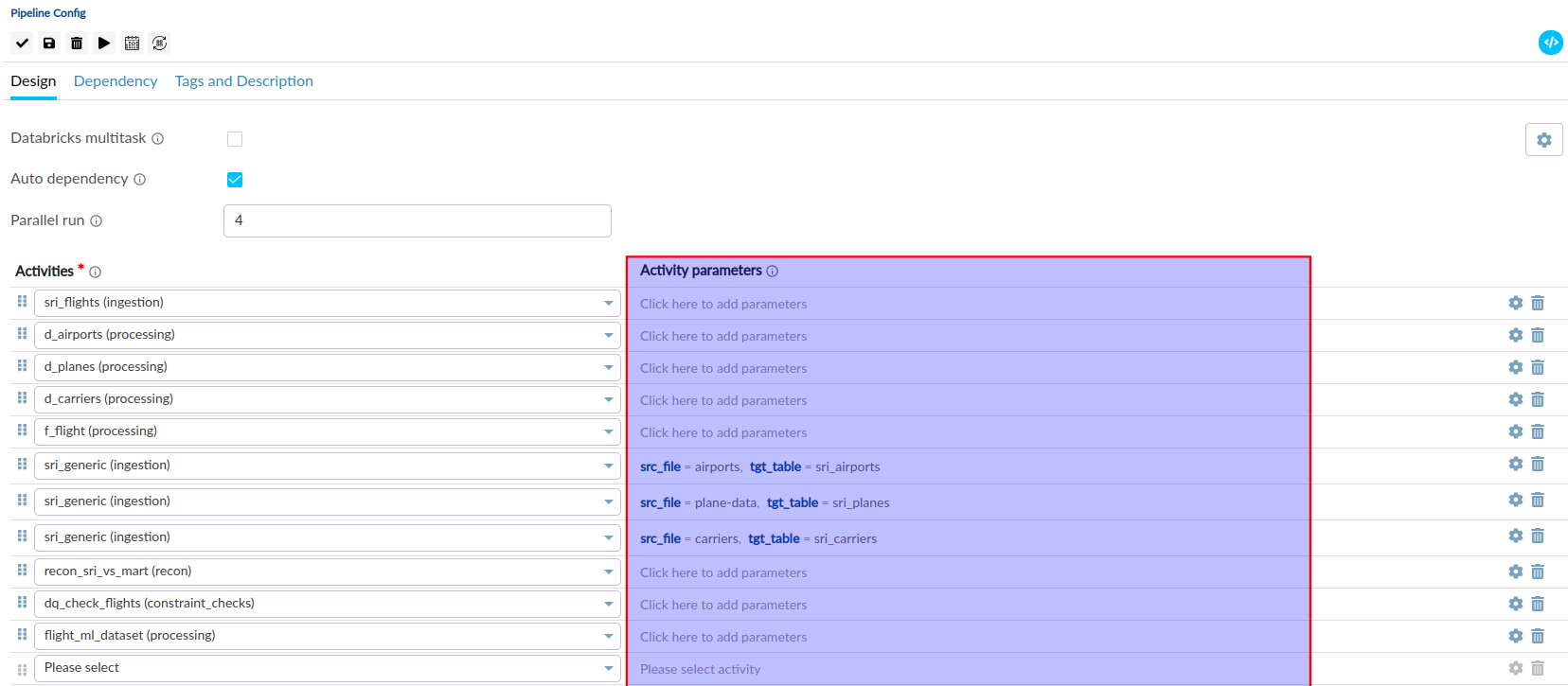
Activity Parameters#
Activity parameters are defined at the pipeline level and can be adjusted during the execution of a pipeline. These parameters serve to control the behavior of the activities, allowing for dynamic configuration, such as specifying the path of a file to be processed.
Defining an Activity Parameter#
To define an activity parameter, follow the steps outlined below:
- In the activity parameters section, click on "Add Parameters".
- Here, you can specify the name and value for the activity parameter.
- Any parameters defined at the pipeline level will have the highest precedence, overriding any lower-level parameter settings.
- For comprehensive and detailed information on Guzzle parameters and Spark parameters please consult the documentation of Guzzle parameters and Spark Parameter.
Activity Settings#
By clicking on the "Settings" button for an activity, you can access and modify the following properties associated with the activity:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Override Databricks Settings | This option allows for updating the Databricks compute settings specifically for the selected activity. Click here to access a comprehensive list of available options. In Databricks multitask pipelines, users can assign newly added computes to specific activity using override databricks settings. |
| Override synapse spark settings | This option allows for updating the Synapse analytics compute settings specifically for the selected activity. Click here to access a comprehensive list of available options |
| Override glue/emr spark settings | This option allows for updating the Glue, EMR EC2 and EMR Serverless compute settings specifically for the selected activity. This option is exclusively available when Guzzle is deployed on the AWS cloud platform. Click here to access a comprehensive list of available options |
| Override spark config | This feature enables the modification of Spark configuration for the activity. Click here to access a comprehensive list of available options |
| Retry | In cases where an activity fails within a pipeline due to various reasons such as network connectivity issues, a retry can be initiated. This feature is only supported when the activity is executed as part of a pipeline. The pipeline will attempt to retry the failed job before moving on to the next job within the same execution thread, assuming parallel jobs are triggered. The Retry properties include:
|
| Timeout properties | The timeout configuration feature allows users to define a specific timeout duration for an activity within a pipeline. If the execution of the activity exceeds the configured timeout period, it will be automatically terminated. This capability provides control over activity execution durations, ensuring efficient pipeline management and resource allocation. It's important to note that this feature is supported exclusively for activities running on Databricks compute. |
Please note that these settings provide granular control over the behavior and configuration of individual activities within the pipeline.
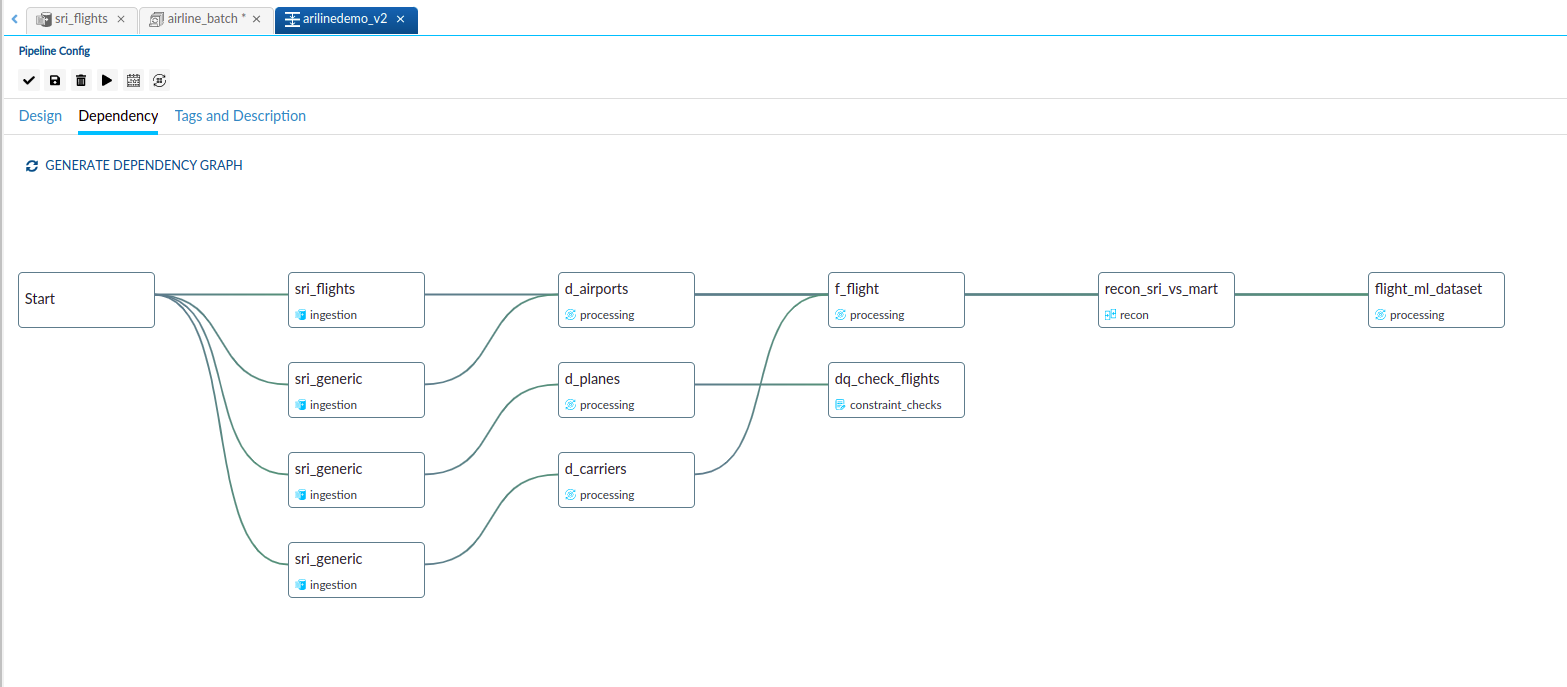
Dependency Graph (Lineage)#
The dependency graph, also known as lineage, provides a visual representation of the ordered flow of the pipeline from its starting point to the endpoint. It allows users to gain a clear understanding of the logical dependencies and relationships between activities within the pipeline.
By referring to the dependency graph, users can visualize the sequential order in which activities are executed, facilitating better comprehension of the overall pipeline structure and ensuring efficient management of dependencies.
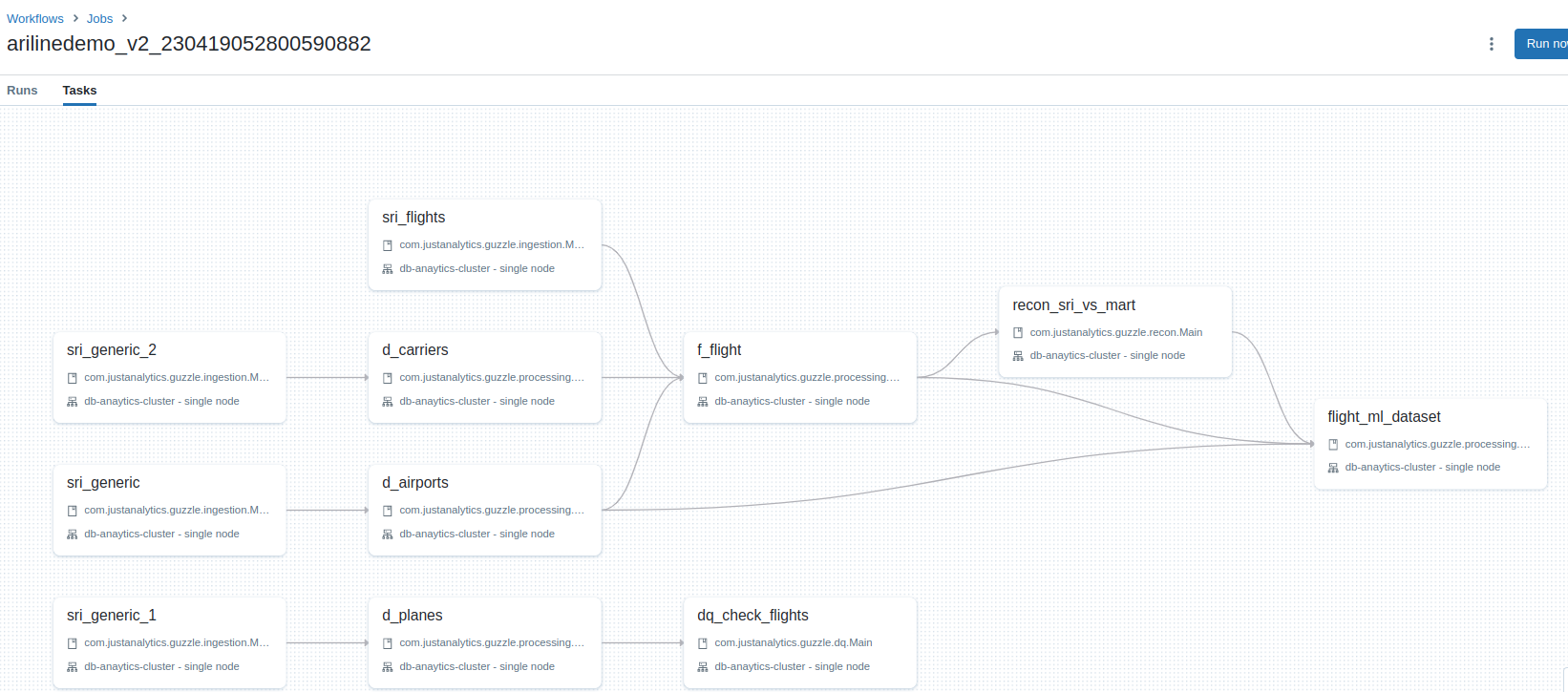
Databricks Multitask Pipeline#
- The Databricks Multitask Pipeline is a pipeline type supported by Guzzle. In this pipeline, Guzzle prepares and submits a collection of activities with their dependencies to Databricks. Databricks takes over the orchestration and execution of the pipeline.
- When utilizing a multitask job in Guzzle, users have the option to configure and utilize new job computes within the pipeline. These job computes can be assigned to specific activities configured in the pipeline.
- By leveraging shared computes, users gain the ability to distribute workloads across multiple computes. This allows for efficient utilization of computational resources, resulting in cost savings and improved pipeline execution time. Sharing workloads between computes optimizes resource allocation and facilitates parallel processing, leading to enhanced performance and faster pipeline execution.
- It's important to note that Databricks multitask pipelines are supported exclusively on Databricks compute.
- In Guzzle, retry settings can be configured for each activity. However, in the case of Databricks multitask pipelines, the retry configuration is submitted to Databricks itself. Therefore, the retry mechanism is performed by Databricks rather than Guzzle, allowing for automatic handling of retries within the multitask job.
- During execution, the multitask pipeline will run from the pipeline thread and wait until its completion before proceeding further.
- Guzzle relies on the Databricks Status API to retrieve the status of multitask pipelines. In the event that the status API is unavailable or unreachable, Guzzle will attempt to retry fetching the status within a certain interval. If unsuccessful, the pipeline will be marked as FAILED, and any NOT_STARTED activities will be marked as ABORTED. Guzzle does not wait by continuously checking the activity status from the Guzzle repository.
Known Limitations#
- Databricks Multitask pipeline do not support processing activities that utilize templates and external activities. If any of these types of activity is configured within a multitask pipeline, Guzzle will return a validation error to notify the user.
- Note: It's important to note that certain processing activities, such as Delta and Azure Synapse Analytics Native with templates, are allowed in Databricks Multitask pipelines.
Dynamic Activity Support in the Pipeline#
- The dynamic activity feature enables users to configure datastores within the pipeline, specifying SQL queries and setting up one or more activities. Similar to other activities, users have access to the same options and configurations for dynamic activities.
- During pipeline execution, the system prepares an activity list based on the results of the SQL query. For each row returned by the query, the configured activities are added to the pipeline. If the query yields zero records, no dynamic activities are added, and the pipeline continues execution with the available activities.
- Users can configure multiple datastores, and within each datastore, multiple activities can be defined.
- To specify the activity name and parameter, users can use either a static value or a placeholder. Placeholders are defined using the format #{column_name}, where the column name acts as a placeholder. During pipeline evaluation, the placeholder will be replaced with the actual value from that column.
- If a user wishes to exclude the creation of dynamic activities or parameter passing, setting a null value or null string in the column name will achieve this.
- When Guzzle detects a null value or null string in the parameter name or value, it will not pass that parameter to the activity. Similarly, if a null value is found for the activity name placeholder, no activity will be added for that particular record.
- Additionally, users can utilize the standard Guzzle placeholder ${placeholder} within the datastore SQL to pass values at runtime, providing further flexibility and customization options.
Placeholder Format#
- When using placeholders in Guzzle, the format to be followed is
#{column_name}. Users should note that placeholders should only contain the column name and cannot be combined with other text or characters. - For example, in the activity name, users cannot use placeholders with additional values such as
ingestion_#{country}_activity. The placeholder#{country}will not be replaced with the actual value. The placeholder format is strictly limited to the column name without any additional text or characters. - To ensure proper functionality and substitution of placeholders, it is essential to adhere to the required format and only utilize placeholders as stand-alone values within the pipeline configuration.
Supported Datastores#
Guzzle supports the following datastores within the pipeline for dynamic activity configuration:
- JDBC
- Azure SQL
- Azure Synapse Analytics
- Redshift
- Snowflake
Pipeline Resume and Partial Run#
Partial Run#
- The partial run feature can be enabled by setting
guzzle.job_group.partial = true. - With partial run enabled, a pipeline can be configured to continue execution even if any jobs within the pipeline fail.
- It's important to note that without enabling partial load, Guzzle will immediately halt the pipeline execution upon encountering any job failure within the pipeline.
- If one or more activities fail, the pipeline status will be marked as WARNING. However, if all jobs fail within the pipeline, the status will be marked as FAILED. Please be aware that the Pipeline Resume feature cannot be used when pipeline has WARNING status.
Resume Pipeline#
- Users can enable the resume feature by setting
guzzle.job_group.resume = true. - This feature allows the pipeline to be resumed from the point of failure.
- Resume feature is only supported for pipelines that have FAILED status. For pipelines with WARNING or SUCCESS status, a new execution will be started instead of resuming the previous run.
- When resuming the pipeline, Guzzle will rerun the activities that have FAILED or are in the NOT_STARTED state. SUCCESS and WARNING activities from the previous run will be skipped. This feature proves beneficial when there is a need to resume execution from a failed job, avoiding the expense of rerunning the entire pipeline from the beginning.
- To resume an individual pipeline, users must provide the exact same business_date and user parameters that were used in the previous execution. If different business_date or user parameters are provided, a new pipeline execution will be initiated instead of resuming the previous one. However, users can pass different values for internal parameters.
note
- During the execution of a Guzzle job, Guzzle internally maintains a heartbeat of the job in the Guzzle repository database. A corresponding entry is created in the heartbeat table, indicating the running state of activities. Guzzle updates this heartbeat table every 5 seconds.
- The Guzzle API thread is responsible for regularly checking the heartbeat value in the heartbeat table. If the heartbeat is not updated within 1 minute, Guzzle will mark the corresponding Activity or Pipeline as ABORTED.
- In certain cases, it has been observed that the database update process in Guzzle takes longer than usual, resulting in the inability to update the heartbeat. As a consequence, the affected Activity or Pipeline will be marked as ABORTED.
- To address this issue, users have the option to adjust the heartbeat setting by navigating to
Manage -> Environment Config -> Timeout and Sync -> Job Heartbeat Configuration -> Job Aborted Timeout. By updating this setting to 300000 (5 minutes), Guzzle will wait for a maximum of 5 minutes to check the status of the heartbeat, allowing sufficient time for the database update to occur. - If a user encounters a Spark OOM exception, the Guzzle activity will be labeled as ABORTED, and the status of the Pipeline/Batch will be set to FAILED