Watermark
Using Watermark for Databases
A watermark represents tracking the last loaded value for one or more columns for a given source table or source SQL to enable loading data incrementally. Using watermark columns is one of the mechanisms used for changed data capture (CDC).
Ingestion activity in Guzzle provides an automated mechanism to track last loaded maximum value for the specified columns which are stored in the watermark table in Guzzle repository. Ingestion activity will include additional predicate on the source table or query to capture the values
Guzzle supports Watermark for all the 5 types of Database Connectors namely:
Delta
Hive
Azure SQL
Azure Synapse Connector
JDBC
How Does a Watermark Work in Guzzle#
"Configure Watermark" section in Source Tab contains following properties for configuring incremental loading for a source table:
| Property | Description | Default Value | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| Watermark Columns | Specify one or more columns that shall be used for watermark tracking Once specified, it will track the maximum value of each of these columns based on incoming source data | None | Yes |
| Watermark filter | To specify custom watermark filter using the watermark columns When left blank Ingestion activity generates automatic filter which is series of AND condition with column value > watermark value. Example: last_modified_dt > '2021-06-17 04:01:46' AND id > '4' | None | No |
| Additional identifier for tracking watermark | If watermark | None | No |
Guzzle first retrieves the old watermark value and compares it with the current watermark value. After that, it copies only the changes from the source database, based on a comparison between the two watermark values. Finally, it stores the new high-watermark value to the target table for Data loading next time.
In Configure Watermark Section specify the Column Name you would like to apply the Watermark to. The allowed values are Timestamps, Dates and Integers.
In the first job cycle Guzzle will load all the Data from the Source table into the Target table and record the maximum value of the specified column.
Now when the next job cycle is run and Guzzle tries to read the Source Table, it will only load the Source Data which is greater than the recorded value in the previous step. (Note: Only when Load type is Incremental which is our Default choice).
The new highest value in the Second Job Cycle will be recorded, and thus the Watermark value will be updated accordingly.
If the user wants to completely refresh the Data the Load Type can be changed to Full.
The Working of the Watermark function can be understood through the Flow Diagram below:

In the image below we consider 2 columns of our Data last_modified_dt which is a Date timestamp and id which is an integer. If we use incremental as our Load Type, in the first job Guzzle will read the entire Data and record the highest values of both columns and use them as incrementing values. If there is no change in the table before the second run then Guzzle will read 0 Parameters or Values in the second run.
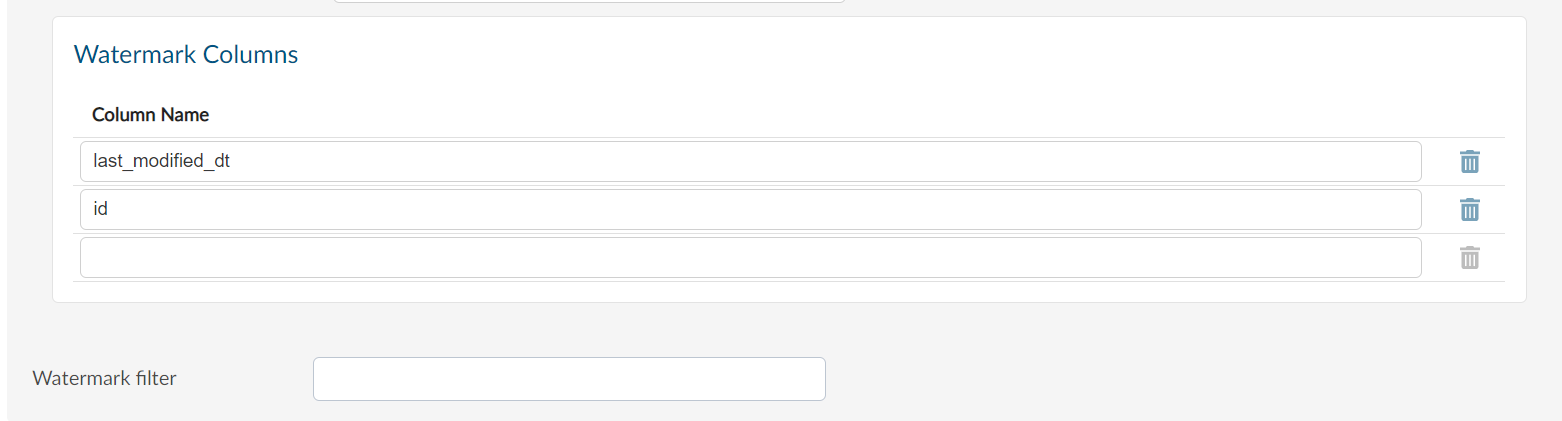
Custom Watermarks or Watermark Filter#
We can create Custom Watermarks by using the Watermark Filter option provided by Guzzle. The Watermark Filter section can be used to specify the condition for our Columns. Only the rows which satisfy the condition will be reflected in the Target Table.
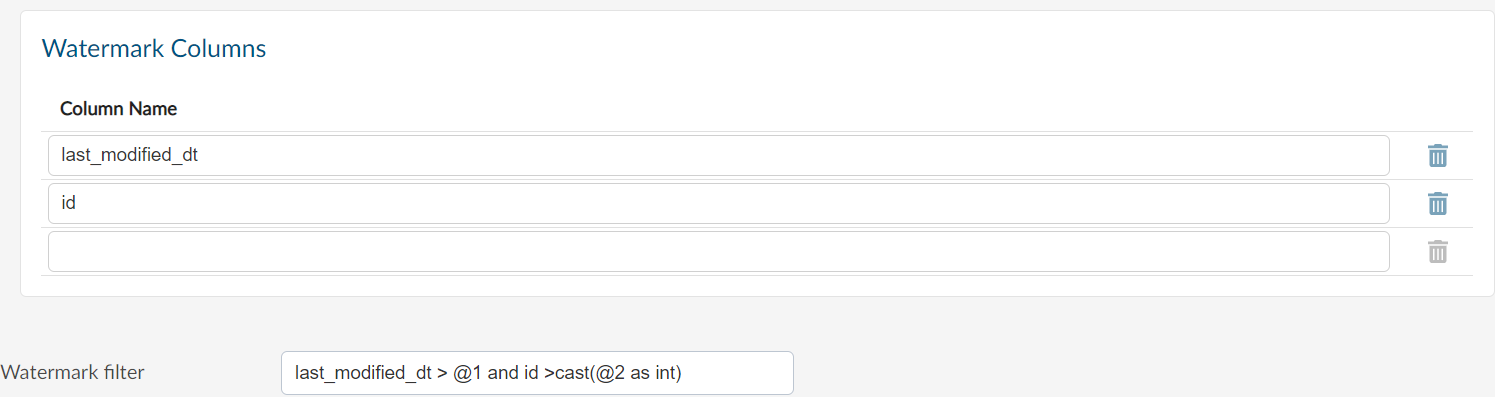
An Example of using the Watermark filter is:
last_modified_dt > @1 and id >cast(@2 as int)
The @1 represent last max value stored in guzzle watermark table for first column
The @2 represent last max value stored in guzzle watermark table for second column
note
The cast function is used in the second test case to ensure that Guzzle reads id as an integer and not a String, as Watermark supports only timestamps and integers.
If Custom Watermark is applied to multiple columns the and condition is used as shown above.
Depending on the typecast database Guzzle passes the values as string to the underlying database for the watermark column.
An example of applying the Watermark technique in MySQL can also be seen in the example below:
insert into customer1_src values (11,'ABC','XYZ','Male',40,'2021-06-17 03:52:25');
create table customer1_tgt(id int, first_name varchar(100), last_name varchar(100), gender varchar(100), age int, last_modified_dt timestamp, refresh_ts timestamp);
Here the insert into statement is used to insert a record into our table.
The second statement uses 2 watermark columns: last_modified_dt timestamp and refresh_ts timestamp.
Custom Watermarks can also be applied to a single column. Instead of applying a standard filter as shown above, we can apply watermarks to a single column for different purposes.
In the above example we can apply the custom watermark to only the last_modified_dt column to fetch Data for let's say the last 7 days. This can be done using the statement below:
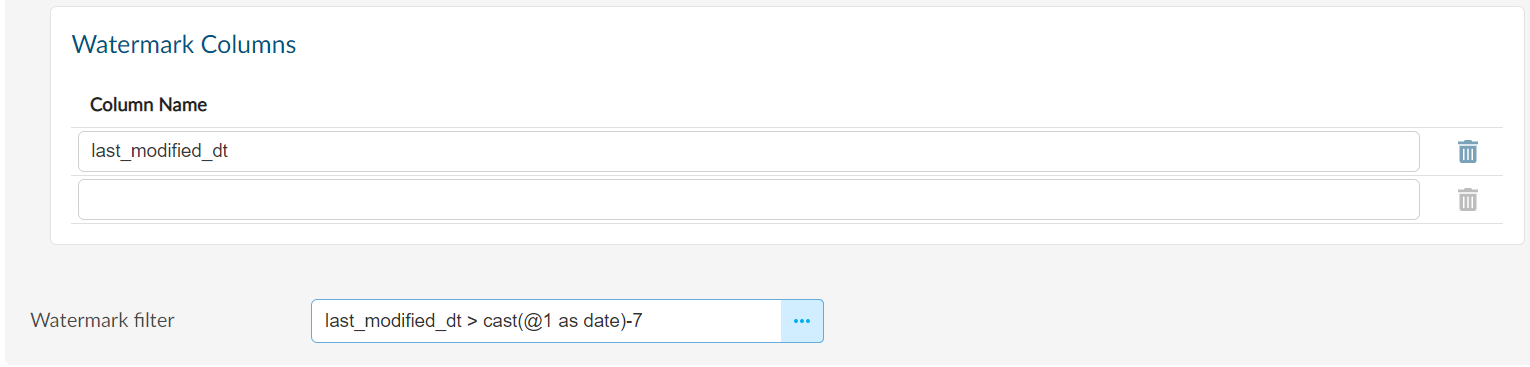
The cast function will convert our max value into a Date, and we then subtract 7. Whatever is the max value it will fetch Data for the last 7 days.